Arrays and Classes
First of all you should have the proper knowledge of the arrays.
If you dont know about array then go to the following link :
Arrays
Arrays and classes can be in two ways :
- Array within classes
- Array of objects
-Array within classes :
In this the data member is declared as an array of the required size.
Syntax :
class class-name
{
private :
datamember[size];
public :
datamember[size];
member function;
};
Example :
#include <iostream.h>
#include <conio.h>
class Student
{
private:
int rollno[4];
int i;
public:
void setRecord();
void display();
};
void Student :: setRecord()
{
cout<<"Enter the rollno's 4 students : ";
for(i=0;i<=3;i++)
{
cin>>rollno[i];
}
}
void Student :: display()
{
cout<<"\n\nRollno are : ";
for(i=0;i<=3;i++)
{
cout<<"\n" << rollno[i];
}
}
void main()
{
clrscr();
Student stud;
stud.setRecord();
stud.display();
getch();
}
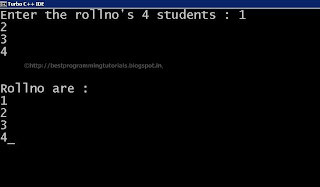
Output :
- Array of objects :
In this case the object is an array of respective size. Means the class can be accessed many
times by a single object.
Syntax :
class class-name
{
private :
datamember;
public :
datamember;
member function;
};
class class-name object[size];
Example :
#include <iostream.h>
#include <conio.h>
class Student
{
private:
int rollno;
int i;
public:
void setRecord();
void display();
};
void Student :: setRecord()
{
cin>>rollno;
}
void Student :: display()
{
cout<<"\n" << rollno;
}
void main()
{
clrscr();
int i;
Student stud[3];
cout<<"Enter 4 roll numbers : ";
for(i=0;i<=3;i++)
{
stud[i].setRecord();
}
cout<<"\n\nYou entered following roll no's : ";
for(i=0;i<=3;i++)
{
stud[i].display();
}
getch();
}
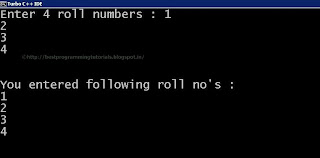
Output :
Prev NEXT




0 comments:
Post a Comment